Analyzing Equilibrium and Redundancy of Indeterminate Structures

While analyzing any indeterminate structure using any method, it is necessary that the solution satisfy the following requirements:
- Equilibrium of the Structure
- Compatibility of the Structure
- Force Displacement Requirements
I. Equilibrium of a Structure
Equilibrium of a Structure is satisfied when the actions (applied loads) and reactions hold the structure at rest. For a finite sized structure, substructure, element or joint, the following six equations must be satisfied:
ΣFx = 0 ΣFy = 0 ΣFz = 0
ΣMx = 0 ΣMy = 0 ΣMz = 0
Number of equations reduces to 3 for a 2D element or structure:
ΣFx = 0 ------------------------(1)
ΣFy = 0 ------------------------(2)
ΣM = 0-------------------------(3)
These equations are known as Equations of Equilibrium. A structure in which all the unknowns can be determined using the Equations of Equilibrium is known as Statically Determinate Structure. While a structure in which all the unknowns cannot be determined using these equations is known as Statically Indeterminate Structure.
II. Compatibility of a Structure
Compatibility of a Structure is satisfied when the various segments of the structure fit together except intentional breaks or overlaps. By compatibility we mean that:
- Members initially connected together remain connected together (the distance between them may have altered due to the deformation)
- Two initially separate points remain separate (do not overlap or move to another common point)
- Cracks or Gaps do not appear as a structure deforms
Consider the indeterminate truss. Each of the members has been elongated. Point A has movedto a new Point A’. However, by compatibility of displacements, the elongations are such that the three members remain connected even after deformation, which is additional information and helps in developing an extra equation or set of equations.
In the following indeterminate propped beam; we know that at the supports A and B there is no deflection i.e.
dA = 0 Also dB = 0
In addition slope at a point of maximum deflection is zero i.e.
dy/dx = 0
At the fixed end rotation is resisted hence i.e.
ΣA = 0
All these equations are known as compatibility equations.
Redundancy of a Structure
Any constrain in a structure when removed and do not cause instability to the structure is known as redundant. Consider the following simply supported beam. The horizontal and vertical reactions at a hinged support A and the only vertical reaction at the roller support B prevent both the translation and rotation of the beam. In other words these supports are sufficient to keep the structure stable.
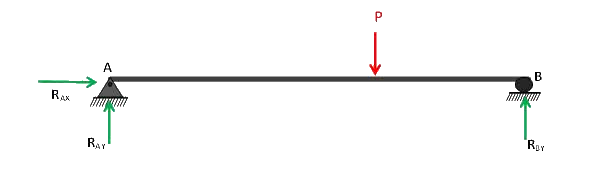
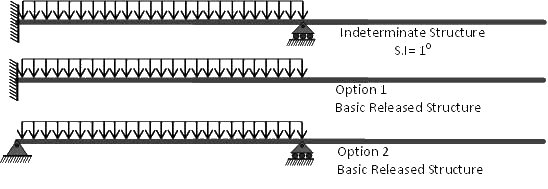
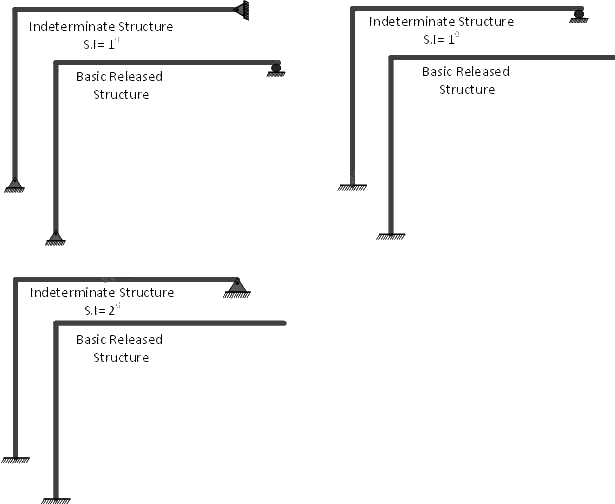
If a third support C is provided between these two, it will make the structure more stable, but its absence is not causing any instability. Thus the vertical reaction provided by this support may be regarded as redundant and can be removed. The structure is then known as basic released structure or primary structure.
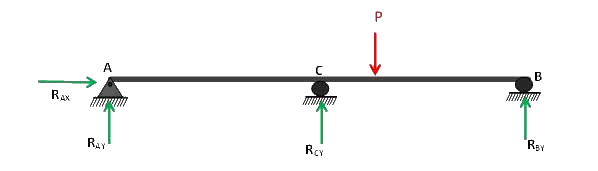
The choice of redundant is increased with this extra support thus if the support B is removed, the structure is still stable. Thus any of the support B or C may be removed except the hinged one, which if removed will cause a parallel system of reactions and thence causing the instability of a structure.
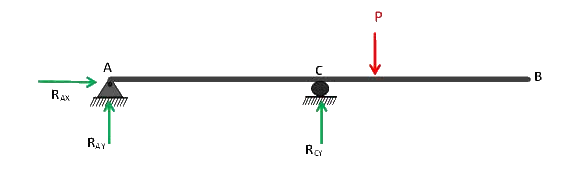
Examples of Redundancy/Basic Released Structures