Functions of Concrete Slab | Definition and Functions
A flat piece of concrete, put on the walls or columns of a structure. It serves as a walking surface but may also serve as a load-bearing member, as in slab homes.
Functions of Concrete Slab
- Load Distribution
- Provide a flat surface
- Sound, heat, and fire insulator
- Fire Resistor
- Contributes to Structural Stability
- Space between the slab and the ceiling can be used to place building facilities - Floors
Load Distribution
Slabs transfer dead loads (self-weight, floor finishes) and live loads (people, furniture, machinery) to beams, columns, and walls.
Example:
-
A residential concrete slab (150mm thick) carries furniture, occupants, and appliances, distributing the weight to the foundation.
Calculation:
-
Self-weight of slab = Thickness × Density of concrete
-
If thickness = 0.15m & density = 25 kN/m³
-
Self-weight = 0.15 × 25 = 3.75 kN/m²
-
Provides a Flat Surface
Slabs create usable floors, roofs, and ceilings, ensuring a smooth surface for walking, working, or placing objects.
Example:
-
Industrial warehouse slabs are designed to withstand heavy machinery and forklift traffic.
Interesting Fact:
-
The thickest concrete slab ever poured was 5.5 meters (18 feet) thick for the Three Gorges Dam in China.
Sound and Heat Insulator
Slabs help regulate temperature and reduce noise transmission between floors.
Example:
-
Hollow core slabs improve thermal insulation in cold climates.
Formula for Heat Loss (Q):
Where:
-
= Thermal conductivity (W/m·K)
-
= Surface area (m²)
-
= Temperature difference (°C)
-
= Thickness (m)
Acts as a Fire Resistor
Concrete slabs provide fire resistance, protecting the structure from collapse.
Example:
-
A 2-hour fire-rated slab can withstand fire for 120 minutes before failing.
Interesting Fact:
-
The World Trade Center used composite steel-concrete slabs to improve fire resistance.
Contributes to Structural Stability
Slabs act as diaphragms, transferring lateral forces (wind, earthquakes) to shear walls and frames.
Example:
-
Flat slabs (without beams) are used in seismic zones for better load distribution.
Calculation for Seismic Load:
Where:
-
= Lateral force (kN)
-
= Mass of slab (kg)
-
= Seismic acceleration (m/s²)
Facilitates Utilities Installation
Electrical conduits, plumbing pipes, and HVAC ducts are often embedded within or below slabs.
Example:
-
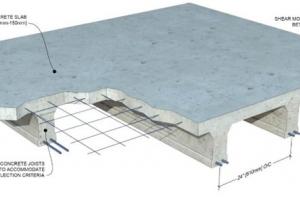
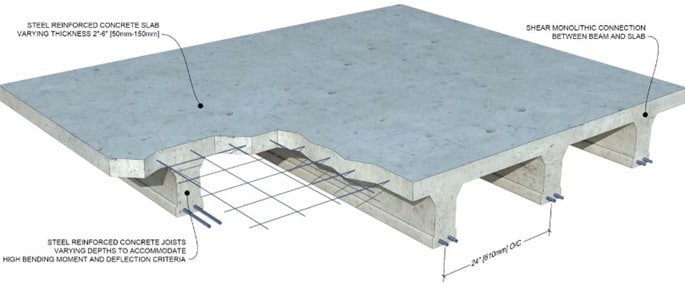
Post-tensioned slabs allow longer spans with fewer columns, making them ideal for parking garages.
Design Considerations in Slab:
- Locate the position of the wall to maximize the structural stiffness for lateral loads
- Facilitates the rigidity to be located at the center of the building
- It's necessary to check the slab deflection for all load cases, both for a short and long-term basis. In general, under full service load, Deflection (d) < L/250 or 40 mm, whichever is smaller.
- It's preferable to perform crack width calculations based on the spacing of reinforcement.
- Good detailing of reinforcement will restrict the crack width to within acceptable tolerances as specified in the codes and reduce future maintenance costs of the building
- Take care of punching shear i.e use more steel or thickness of concrete where there is chance of punching shear in the concrete slab. To increase shear capacity at the edges of walls and columns embed shear studs or stirrup cages in the slab.
- Check for lateral stability
Methods of Design of Slab
- The finite element analysis
- The simplified method
- The equivalent frame method
Design and Analysis of Slab in SAP2000