Applications of Bitumen in Civil Engineering

Introduction to Bituminous materials
The term bituminous materials is generally used to denote substances in which bitumen is present or from which it can be derived. Bitumen is defined as an amorphous, black or dark-colored, (solid, semi-solid, or viscous) cementitious substance, composed principally of high molecular weight hydrocarbons, and soluble in carbon disulfide.
For civil engineering applications, bituminous materials include primarily aphalts and tars. Asphalts may occur in nature (natural asphalts) or may be obtained from petroleum processing (petroleum asphalts). Tars do not occur in nature and are obtained as conden-sates in the processing of coal, petroleum, oil-shale, wood or other organic materials. Pitch is formed when a tar is partially distilled so that the volatile constituents have evaporated off from it. Bituminous mixtures are generally used to denote the combinations of bituminous materials (as binders), aggregates and additives.
This article presents the basic principles and practices of the usage of bituminous materials and mixtures in pavement construction. In recent years, the use of tars in highway construction has been very limited due to the concern with the possible emission of hazardous flumes when tars are heated.
Applications of Bitumen in scientific and engineering processes
Uses of Bitumen in Civil Engineering
Following is the list of applications of bitumen in real life:

-
Hydraulics & erosion control Catchment areas, basins
-
Dam grouting
-
Dam linings, protection
-
Dyke protection
-
Ditch linings
-
Drainage gutters, structures
-
Embankment protection
-
Groynes
-
Jetties
-
Levee protection
-
Mattresses for levee & bank protection
-
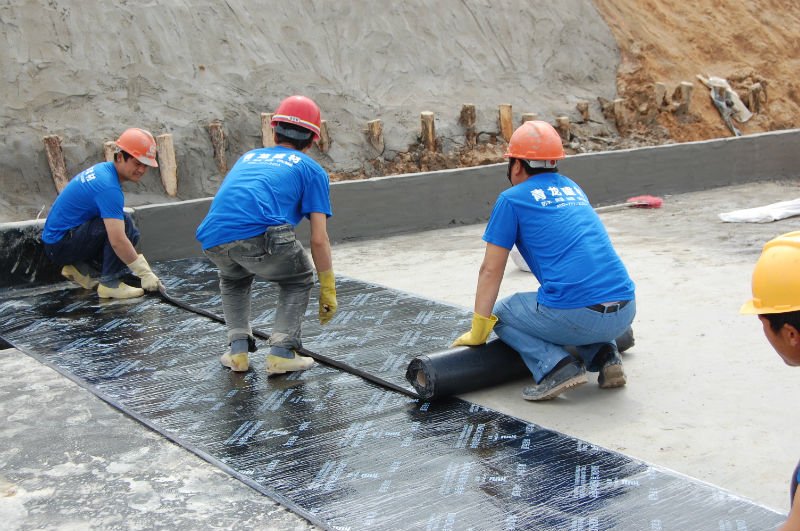
Membrane linings, waterproofing
-
Reservoir linings
-
Revetments
-
Sand dune stabilization
-
Sewage lagoons, oxidation ponds
-
Swimming pools
-
Waste ponds
-
Water barriers
-
Backed felts