What is Varnish and Types of Varnishes

Definition
Varnishes are more or less transparent liquids which are used to provide a protective surface coating in much the same way as paints do” At the same time they allow the original surface to show but add a lustrous and glossy finish to it. All varnishes have basically the same components as paints.
What is Varnish? Varnish is a transparent, hard, protective finish or film primarily used in wood finishing but also for other materials. Varnish is traditionally a combination of a drying oil, a resin, and a thinner or solvent. Varnish finishes are usually glossy but may be designed to produce satin or semi-gloss sheens by the addition of "flatting" agents.
Types of Varnishes
Natural Resin Varnishes:
Body made from natural resin obtained from certain trees. Natural resin is obtained from living trees or from fossils(which are superior) Vehicle in varnish is the same as used in oil-based paint. Resins dissolved in oil ► mixture heated to temperature (500-600OF) depending on the amount of gloss required. Oil and natural resin varnish ► OLEO RESINOUS varnish. Thinner and dryers used in varnish are the same as used in oil-based paints. Natural resin varnishes are made from resins that are extracted directly from natural sources, such as trees or insects. These resins are often dissolved in solvents and used as coatings.
- Examples:
- Shellac: Shellac is a natural resin varnish derived from the secretions of the female lac bug. It has been used for centuries and is known for its excellent adhesion, quick drying time, and glossy finish. Shellac is often used on wood surfaces and is also used in food-safe applications.
- Rosin Varnish: Rosin, derived from pine tree resin, is used to make varnishes for string instruments like violins, violas, and cellos. It provides a protective and resonant coating that enhances the tonal qualities of the wood.
Modified Natural Resin Varnishes:
Made from natural resin ► altered by chemical action. Common resin is heat-treated with glycerin to form a gum. This gum is treated as the body for the varnish. Less expensive varnish than the oleo resinous varnish. Modified natural-resin varnishes are varnishes that incorporate natural resins as their base but are modified or enhanced with additives or synthetic components to improve their performance and characteristics
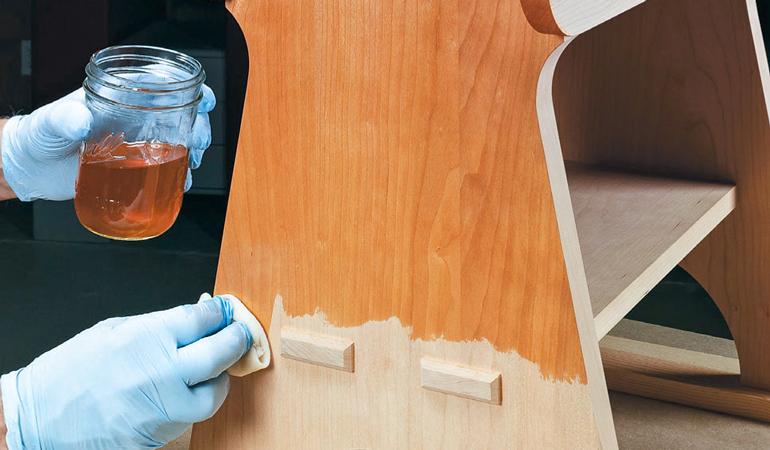

- Examples:
- Polyurethane Varnish: Polyurethane varnish is a widely used modified natural-resin varnish. It contains natural resins but is combined with synthetic polyurethane to create a durable and protective finish. It is highly resistant to moisture, chemicals, and wear, making it suitable for wooden floors, furniture, and outdoor applications.
- Alkyd Varnish: Alkyd varnish is made by combining natural resin with alkyd resins, which are synthetic. This varnish offers good durability, hardness, and UV resistance. It's often used for woodwork and decorative finishes.
- Epoxy Varnish: Epoxy varnish is a two-component coating that combines epoxy resins with a hardener. It provides exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and a high-gloss finish. It's used on various surfaces, including concrete, metal, and wooden boats.
Synthetic Resin Varnish:
Synthetic resin varnish, also known as synthetic varnish or acrylic varnish, is a type of protective coating used to enhance the appearance and durability of surfaces, such as wood, metal, and certain plastics. Unlike natural resin varnishes, which are derived from plant or insect sources, synthetic resin varnishes are formulated using synthetic resins, which are often derived from petrochemical sources. Here's a more detailed explanation of synthetic resin varnishes:
Key Characteristics of Synthetic Resin Varnish:
Composition: Synthetic resin varnishes primarily consist of synthetic resins as the film-forming component. These resins can be acrylics, polyurethanes, epoxies, or a combination of various synthetic materials.
Versatility: Synthetic resin varnishes are versatile and can be used on a wide range of substrates, including wood, metal, concrete, plastics, and even some painted surfaces. They adhere well to many materials.
Durability: These varnishes are known for their durability and excellent protective qualities. They provide a strong and resilient layer that shields the underlying material from damage due to moisture, chemicals, UV radiation, and physical wear.
Fast Drying: Many synthetic resin varnishes have relatively short drying times, which allows for quicker project completion compared to some other types of varnishes.
Clarity: Acrylic-based synthetic resin varnishes are known for their clarity, making them suitable for projects where maintaining the original appearance of the surface is essential. They do not yellow over time, which is a common issue with some natural resin varnishes.
Low Odor: These varnishes tend to have a low odor, making them more convenient to work with, particularly in indoor or enclosed spaces.
Common Uses and Examples:
Wood Finishes: Synthetic resin varnishes are widely used on wooden surfaces, including furniture, cabinets, and wood flooring. They enhance the wood's natural beauty, provide protection against stains and moisture, and can be available in various sheens, from matte to high-gloss.
Artwork: Acrylic varnishes are used to protect and preserve paintings and artwork. They are available in various sheens to achieve the desired appearance, from a matte finish to a glossy shine.
Automotive Finishes: Many automotive clear coats and finishes use synthetic resin varnishes to protect the vehicle's paint and provide a glossy appearance.
Architectural Coatings: These varnishes are employed in architectural applications to protect and extend the life of structures, such as steel and concrete surfaces while maintaining their aesthetic appeal.
DIY and Craft Projects: Synthetic resin varnishes are popular among hobbyists and crafters for sealing and finishing various projects, such as resin art, woodworking, and more.
Marine Coatings: Epoxy-based synthetic resin varnishes are used for protecting boats, yachts, and marine equipment against the harsh conditions of saltwater and sun exposure.
Synthetic resin varnishes offer numerous benefits in terms of versatility, durability, and aesthetic qualities. They are suitable for various applications and have become an essential part of protecting and beautifying surfaces in both industrial and consumer settings.
- Synthetic varnish produced by the plastic industry
- Chemicals used include nitrocellulose, amino resins, silicon, etc.
- Vehicle most often the same as for oleo resinous varnish
- Coal tar derivatives may be used as thinners
- The dryer is also the same as for other types of varnishes
Classification of Varnishes
Long oil varnish:
- Definition: Long oil varnish contains a higher proportion of natural or synthetic oils in its formulation compared to the resin content. The oil content exceeds 50%.
- Characteristics:
- Flexible: Long oil varnishes tend to be more flexible and elastic, making them suitable for surfaces that experience some degree of movement or expansion and contraction, such as wooden surfaces.
- Slower Drying: They have a longer drying time due to the higher oil content, which can be advantageous for some applications.
- Enhanced Clarity: Long oil varnishes often have good transparency, making them suitable for applications where preserving the natural appearance of the substrate is important.
- Applications: Long oil varnishes are commonly used on wooden furniture, wooden boats, and musical instruments to provide a flexible and durable protective coating.
- Long oil contains 40 to 100 gal of oil per 100 lbs of resin.
- Takes a longer time to dry
- Moderate gloss
- Marine and spar varnish belongs to this group
- Tung oil used ► impervious to water
Medium oil varnish:
- Definition: Medium oil varnish contains a balanced ratio of resin and oil, with the oil content typically ranging between 40% and 50%.
- Characteristics:
- Balanced Attributes: Medium oil varnishes offer a compromise between the flexibility of long oil varnishes and the faster drying times of short oil varnishes.
- Versatile: They are suitable for various applications where a balance of durability, flexibility, and drying time is required.
- Good Clarity: Depending on the specific formulation, medium oil varnishes can offer good clarity and gloss.
- Applications: Medium oil varnishes are often used for general woodworking, architectural finishes, and on surfaces that require a combination of protection and aesthetic appeal.
- Medium oil contains 12 to 40 gal of oil per 100 lbs of resin
- They dry faster and harder
- Harder film than long-oil varnish but are not impervious to water
- Floor varnish belongs to this group
- Short oil resins:
Short oil contains 5 to 12 gal of oil per 100 lbs of resin. Dry rapidly ► form a hard, brittle film that withstands much rough usage. Polishing varnish belongs to this group.
- Definition: Short oil varnishes, sometimes referred to as short oil resins, have a higher proportion of resins and a lower content of oils. The oil content is typically less than 40%.
- Characteristics:
- Faster Drying: Short oil varnishes dry relatively quickly due to the lower oil content. This can be advantageous when a faster project turnaround is needed.
- Rigidity: They tend to produce a harder and more rigid finish, making them suitable for surfaces that do not undergo significant movement.
- Lower Clarity: Short oil varnishes can be less clear or transparent compared to other varnish types.
- Applications: Short oil varnishes are commonly used on surfaces like metal, concrete, and some interior architectural elements. They are also used in industrial and marine applications where rapid drying and rigidity are desired.
How to Varnish
Applying varnish is a common finishing technique used to protect and enhance the appearance of various surfaces, including furniture, wooden floors, and certain crafts. The process of varnishing is generally similar, but specific techniques may vary depending on the type of varnish and the surface being finished. Here, I'll provide a general overview of how to varnish, along with some specific instructions for a varnish finish, floor varnish, and oil varnish.
General Steps for Varnishing:
-
Preparation:
- Ensure that the surface to be varnished is clean, dry, and free from dust or debris. Sand the surface if needed to achieve a smooth finish.
- If you're refinishing an old varnished surface, remove any existing varnish or finish.
-
Choose the Right Varnish:
- Select the appropriate varnish for your project. Consider factors such as the type of surface, the level of durability required, and the desired finish (e.g., gloss, satin, matte).
-
Application:
- Stir the varnish thoroughly but gently before use. Avoid shaking it vigorously, as this can introduce air bubbles.
- Apply the varnish evenly using a high-quality brush, foam applicator, or a clean, lint-free cloth. Work in the direction of the grain, if applicable.
-
Coats:
- Apply multiple thin coats of varnish rather than a single thick coat. Allow each coat to dry thoroughly before applying the next. Follow the manufacturer's recommended drying times.
-
Sanding Between Coats:
- For a smoother finish, lightly sand the surface with fine-grit sandpaper (e.g., 220-grit) between coats to remove any imperfections or rough spots. Wipe away the dust before applying the next coat.
-
Final Coat:
- The final coat should be applied with care and precision to achieve the desired finish. Sand lightly, if necessary, after the final coat has dried.
-
Curing:
- Varnish typically takes time to fully cure and harden. This process can take several days to a few weeks, depending on the varnish and environmental conditions.
Specific Instructions for Different Types of Varnish:
-
Varnish Finish:
- Follow the general steps outlined above.
- Varnish finishes can be applied to a wide range of surfaces, from wood to metals, and are available in different sheens (gloss, satin, matte). Choose the sheen that best suits your project.
-
Floor Varnish:
- Prior to varnishing a wooden floor, ensure the floor is sanded down to a smooth surface.
- Apply a minimum of three coats of floor varnish, allowing each coat to dry completely before walking on it.
- Consider water-based floor varnish for quicker drying and lower odor, or oil-based varnish for a more traditional, durable finish.
-
Oil Varnish:
- Oil varnish is typically applied in thin coats using a brush, foam pad, or cloth.
- After each coat, wipe off any excess varnish to prevent streaks or blotches.
- Allow sufficient drying time between coats, and sand lightly between coats if necessary.
Proper varnishing techniques, including surface preparation and applying multiple thin coats, will help you achieve a beautiful, durable finish that enhances the appearance and protection of your chosen surface.
Plasters
Overall, it can be stated that the improved element performed better than the traditional element in the series of earthquake simulations. This statement is based on an assessment of the risk of causing injury posed by each structure. The walls of the traditional corners were independent and unstable. Any additional force, such as another tremor or a strong wind or impact, could cause either wall to topple over, in an inward or outward direction. This represents an unacceptable level of risk. These buildings are one of the most deficient building systems from earthquake-resistance point of view. The main deficiencies include excessive wall thickness, absence of any connection between the two withes of the wall, and use of round stones (instead of shaped ones).
Distempers
They are paints used for the treatment of masonry walls. Water instead of oil is used as a vehicle ► known as water-paint too. Powdered white chalk and glue boiled in water are mixed. Usually colored by mixing different pigments. All Distempers are mixed with water only before being used. Distemper affected by weathering conditions and takes off if washed ► to be used only in interior works. Cheap, durable, and easy interior finish. Should be applied on a clean and dry surface.