How to Design Dams
Designing a dam is a complex process that requires a thorough understanding of civil engineering principles, geology, hydrology, and other related disciplines. Here are the general steps involved in the design of a dam:
-
Identify the dam site: The first step in designing a dam is to identify a suitable location for the dam. Factors to consider include the topography of the area, the geology of the site, the size of the reservoir, and the intended use of the dam.
-
Conduct a site investigation: Once a potential site has been identified, a detailed site investigation must be conducted to assess the site's geology, hydrology, and other relevant factors. This may involve drilling boreholes, taking soil and rock samples, conducting geophysical surveys, and analyzing data from previous studies.
-
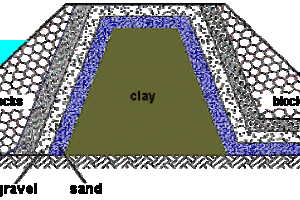
Determine the type of dam: Based on the site investigation and other factors, the type of dam that will be constructed must be determined. The most common types of dams include embankment dams, concrete gravity dams, arch dams, and buttress dams.
-
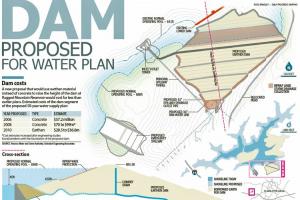
Calculate the dimensions of the dam: Once the type of dam has been selected, the dimensions of the dam must be calculated based on the required storage capacity of the reservoir, the expected water level, and other factors.
-
Design the foundation: The foundation of the dam must be designed to ensure that it can support the weight of the dam and withstand the forces exerted by the water in the reservoir. This may involve excavating the foundation area and installing a grout curtain or other foundation treatment.
-
Design the spillway: The spillway is a critical component of the dam that is used to control the release of water from the reservoir. It must be designed to handle the maximum expected flow of water and to prevent damage to the dam during flood events.
-
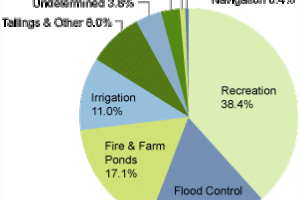
Design the outlet works: The outlet works are used to release water from the reservoir for various purposes, such as irrigation or hydroelectric power generation. They must be designed to ensure a reliable and safe supply of water.
-
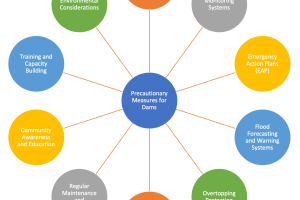
Perform safety analyses: Once the dam has been designed, safety analyses must be conducted to assess the risk of failure and identify any potential hazards. This may involve using computer models to simulate various scenarios, such as floods or earthquakes.
-
Obtain necessary permits: Before construction can begin, the necessary permits must be obtained from regulatory agencies. This may involve obtaining approvals for environmental impact assessments, water use permits, and other requirements.
-
Construct the dam: Finally, the dam can be constructed using the design plans and specifications. This may involve excavating the foundation, constructing the spillway and outlet works, and placing the embankment or concrete.
It is important to note that the specific steps involved in designing a dam can vary depending on the type of dam and the local regulations and requirements. Additionally, the design of a dam is a complex process that should only be undertaken by experienced professionals with the necessary knowledge and expertise.
Points for Design of Dam
Some points to keep in mind during the design of a dam are as follows:
- The construction of the dam should be economical
- The dam should be feasible to construct e.g availability of labor, material, experienced and skilled personnel etc.
- The dam should be durable and safety against erosion should be provided i.e it should have a longer lifetime.
- It should be stable.
- The saturation line of the dam should be in the downstream face.
- The dam body as well as the foundation of the dam should be safe from piping
- Environmental disturbance should be minimum