Types of Grit Chambers in Waste Water Treatment
The objectives of Grit Chambers are:
- Protect moving mechanical equipment from abrasion and abnormal wear
- Reduce formation of heavy deposits in pipelines, channels and conduits
- Reduce the frequency of digester cleaning caused by excessive accumulation of grit
Types of Grit Chamber
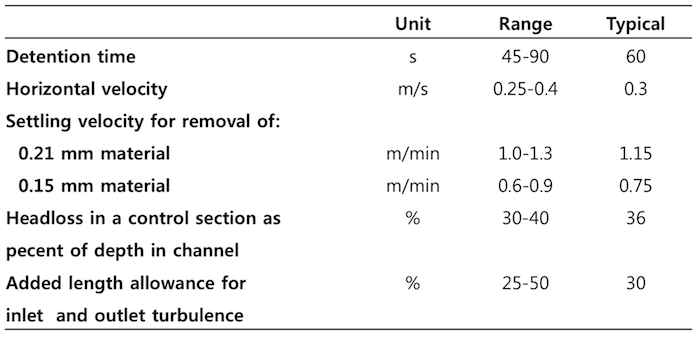
1. Horizontal flow (Rectangular or square) (configuration type)
Designing a Rectangular horizontal flow type grit chamber:
- Cross-sectional area, Ax = (Qdesign / Vh) for each unit (Vh ≈ 1 ft/sec), depth ≈ 3-5 ft
- Assuming (tD = 1-2 minutes), determine the length L = Vh * tD (Add 10% additional)
- Check the SLR (1200-1700 m3/m2-day) and Vs (≥ 0.01 m/sec). Grit produced is about 1.5 ft3/ML of wastewater flow. Add to depth {1ft FB + grit}
2. Aerated Grit Chamber
Basic Info
- Air is introduced along one side of a rectangular tank to create a spiral flow pattern perpendicular to the flow through the tank.
-
If the velocity is too great, grit will be carried out of the chamber; if it is too small, organic material will be removed with the grit.
-
Normally designed to remove 0.21-mm-diameter or larger, with 2-5-minute detention periods at the peak hourly rate of flow
- Air diffusers are located about 0.45 to 0.6m above the normal plane of the bottom.
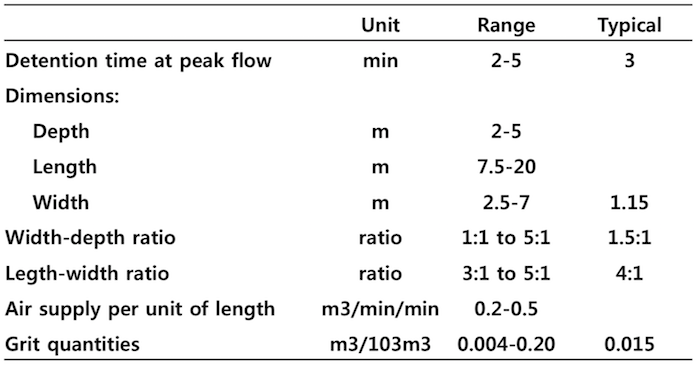
Designing an Aerated grit chamber:
- Assume a “tD” (3-4 min), determine the volume of the basin.
- Assume a depth (D = 08-15 ft), determine the surface area of the basin. And check the SLR (1200-1700 m3/m2-day)
- The amount of grit produced is about 1.5 ft3/ML of wastewater flow. Add suitable depth from grit and free board.
- Calculate the amount of air required (0.2-0.5 m3/min/m length of the tank)