How to find Bearing Capacity of Soil
Methods of bearing capacity determination
-
Analytic method i.e. through bearing capacity equations like using Terzaghi equation, Meyerhof equation, Hansen equation etc
-
Correlation with field test data e.g. Standard penetration test (SPT), Cone penetration test (CPT) etc
-
On site determination of bearing capacity e.g Plate load test, Pile load test
- Presumptive bearing capacity (recommended bearing capacity, in various codes)
Following are the methods:
- Analytical Method of Bearing capacity determination
Analytical Method
Lower Bound Failure
Lower bound failure states that “If an equilibrium distribution of stress can be found which balances the applied load and nowhere violates the yield criterion, the soil mass will not fail or will just be at a point of failure i.e. it will be a lower bound estimate of capacity. Consider the equilibrium conditions in soil under the footing load. When the foundation pushes into the ground, stress block 1 has principal stresses, as shown. The push into the ground however, displaces the soil on the right side of the line OY laterally, resulting in the major principal stress on block 2 being horizontal as shown. When the two blocks are adjacent to each other at the vertical line OY, then
Some Formulae
Upper Bound theorem
Upper bound theorem states that “If a solution is kinematically admissible and simultaneously satisfies equilibrium failure must result” i.e. it will be an upper bound estimate of capacity. For a possible upper bound, consider failure surface as semicircle. Taking moment about O
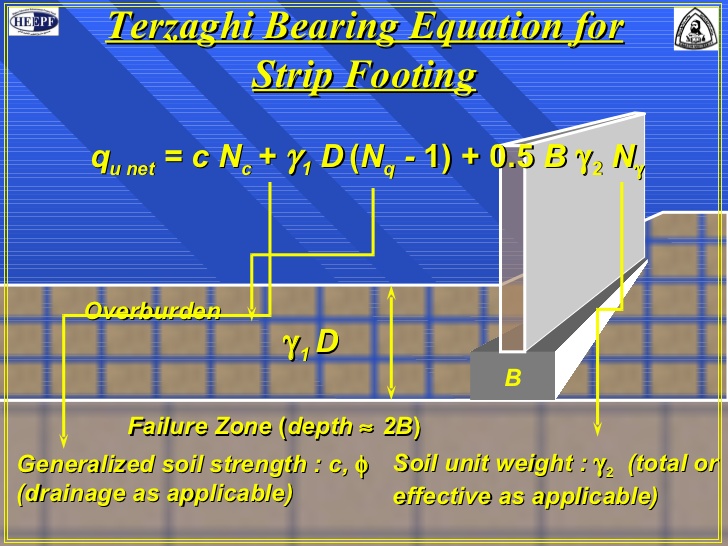
Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation (1943)
Terzaghi developed a general formula for ultimate bearing capacity of spread footing foundation under the following assumptions:
- The depth of the footing is less than or equal to its width (D, B)
- The foundation is rigid and has a rough bottom
- The soil beneath the foundation is homogeneous semi-infinite mass
- Strip foundation with a horizontal base and level ground surface under vertical loads.
- The general shear mode of failure governs and no consolidation if the soil occurs (settlement is due only to shearing and lateral movements of the soil)
- The shear strength of the soil is described by s = c + σ tan
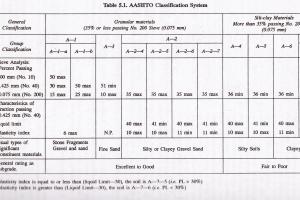
Presumptive Soil Bearing Values by Soil Description
| Presumptive Load Bearing Value (psf) | Soil Description |
|---|---|
| 1500 | Clay, Sandy Clay, Silty Clay, Clayey Silt, Silt and Sandy Silt |
| 2000 | Sand, Silty Sand, Clayey Sand, Silty Gravel and Clayey Gravel |
| 3000 | Gravel and Sandy Gravel |
| 4000 | Sedimentary Rock |
| 12000 | Crystalline Bedrock |