Seepage through Earth Filled Dams and Seepage Control
Dam seepage refers to the movement of water through or under a dam structure, which can lead to potential issues such as reduced dam stability or leakage. The analysis and prediction of dam seepage typically involve hydraulic and geotechnical considerations, such as groundwater flow modeling, seepage control measures, and dam safety assessments. Seepage through the dams is the most damaging factor for dams.
Flownet
Flowlines
Flow channel: Space between two consecutive flow lines is called flow path/flow channel
Equipotential lines
Location of phreatic surface / phreatic line / top flow line
Properties of flownet:
- Each flow path transmits the same quantity of seepage.
- The area bounded by two consecutive flow lines and equipotential lines is a square.
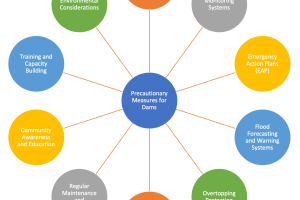
Seepage Control in Dams
Seepage control in dams is a critical aspect of dam design and construction aimed at managing and mitigating the movement of water through or under the dam structure. Seepage can potentially lead to dam failure, erosion of the foundation, and other safety concerns. Therefore, effective seepage control measures are implemented to ensure the stability and integrity of dams. Here are some commonly employed seepage control methods in dams:
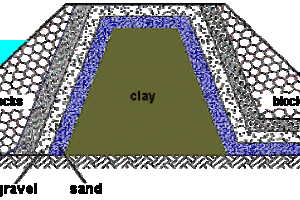
1. Impermeable Core: One of the primary seepage control measures is the construction of an impermeable core within the dam. The core is typically made of compacted clay or concrete, which is a barrier to prevent seepage through the dam body. The core is designed to have low permeability to restrict the flow of water.
2. Filters: Filters prevent the migration of fine particles from the foundation or embankment materials into the core or drainage system. They are typically composed of well-graded granular materials such as sand and gravel. The filters allow water to pass through while preventing the movement of finer particles that could clog the drainage system or affect the dam's stability.
3. Grouting: Grouting involves injecting grout material into the foundation or embankment to fill voids, fractures, or permeable zones. This helps to reduce seepage paths and improve the overall impermeability of the dam. Different types of grouting methods, such as curtain grouting or pressure grouting, may be employed depending on the specific seepage conditions.
4. Cutoff Walls: Cutoff walls, also known as diaphragm walls or seepage cutoffs, are constructed to create a vertical barrier within the foundation to control seepage. Cutoff walls can be made of concrete, steel sheet piles, or other impermeable materials. They are designed to intersect potential seepage paths, such as permeable layers or fractures, and prevent water flow.
5. Drainage Systems: Effective drainage systems are crucial for managing seepage within and around the dam. These systems consist of various elements such as toe drains, horizontal drains, chimney drains, and relief wells. They help to collect and control seepage water, reducing excess pore pressures and maintaining the stability of the dam.
6. Upstream Blanket/Toe Drain: In some cases, an upstream blanket or toe drain is installed along the downstream face of the dam to collect seepage water and prevent it from reaching the downstream slope. The collected water is then directed to the drainage system or released safely downstream.
7. Erosion Protection: Seepage can cause erosion on the downstream face of the dam due to the exit of water under high pressure. To prevent erosion, erosion protection measures such as riprap (layer of large stones) or concrete revetments may be used to dissipate the energy of the seepage flow.
It's important to note that the specific seepage control measures implemented for a dam depending on the site-specific conditions, geological characteristics, and engineering considerations. The design and implementation of seepage control measures involve a comprehensive assessment of potential seepage paths, hydraulic analysis, and review of the long-term performance and safety of the dam structure.