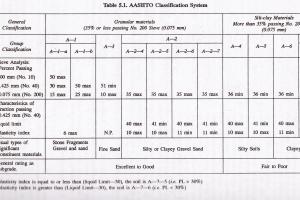
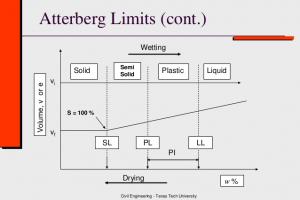
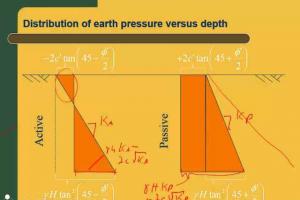
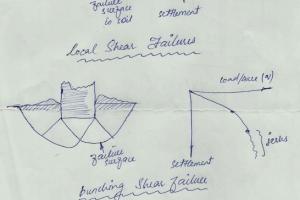
To Determine the Specific Gravity of Soil

ASTM Designation: C128
Apparatus
Sieve #4, balance, electric oven, pycnometer.
Theory
Specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the weight of given volume of material to the weight of an equal volume of water.
G = density of soil/density of equal volume of water
G = mass of dry soil/mass of and equal volume of water.
Procedure
- Take at least 25g of soil which has been passed through sieve#4 and place it in an oven at fixed temperature of 105-110 °C for 24 hours to dry it completely.
- Clean and dry the pycnometer thoroughly and find its mass (M1).
- Find the mass (M2) of pycnometer by placing dried soil in it.
- Add sufficient quantity of water to fill the pycnometer up to the given mark and then find mass of the pycnometer ( m3) and its content.
- Empty the pycnometer then fill it with water up to the same level. Now find the mass (M4) of the pycnometer having water in it.
- Determine the specific gravity of the given soil sample.
Precautions
- The graduated cylinder used should be cleaned.
- Dry the coarse aggregate so that it does not absorb moisture otherwise it will not give the desired results.
- All the readings of mass should be noted carefully.
Practical applications
- The value of specific gravity helps us to some extent in identification and classification of soil.
- It gives the idea about the suitability of a given soil as a construction material.
- It is utilized in calculating voids ratio, porosity, and degree of saturation if the density or unit weight and water content are known.