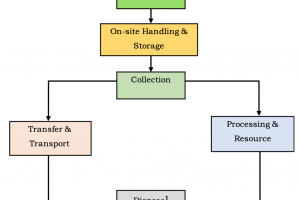
Purpose and Objectives of Urban Drainage System

Objectives of Urban Drainage Systems
The four major objectives of drainage and sewer systems are:
- Public health and safety
- Environmental protection
- Sustainable development
- Occupational health and safety
Drain and Sewer systems are provided in order to prevent the spread of diseases by:
- Preventing contact with fecal and other waterborne waste,
- Protecting drinking water sources from contamination by waterborne waste and
- Carrying runoff and surface water away while minimizing hazards to the public.
Additionally, the impact of drain and sewer systems on the receiving waters shall meet the requirements of national regulations (NEQS) or the relevant authority.
Purpose of Urban Drainage Systems
The purpose of Urban drainage is
- To maintain such an environment that does not affect public health in general.
- The creation of such conditions of living will not result in a serious outbreak of epidemic diseases.
- It is the control of environmental pollution, improving environmental quality to enable a healthy ecosystem and comfortable habitation for humans.
- It is a preventive measure for the preservation of the health of the community in general and individuals in particular.
Sewer systems should be designed, constructed, operated, maintained, and rehabilitated in such a way that they are sustainable and can be operated with the minimum use of energy.
The purpose and objectives of an urban drainage system are as follows:
1. Stormwater Management:
The primary purpose of an urban drainage system is to manage stormwater effectively. It aims to collect, convey, and control the runoff generated during rainfall events, preventing flooding and minimizing damage to urban areas. By efficiently channeling stormwater away from built-up areas, the drainage system helps maintain the safety and functionality of the urban environment.
2. Flood Prevention and Control:
One of the key objectives of an urban drainage system is to prevent and control flooding. It includes the design and implementation of infrastructure, such as storm sewers, culverts, and retention ponds, to safely convey excess stormwater away from vulnerable areas. The system is designed to accommodate various rainfall intensities and prevent water accumulation that can cause property damage and jeopardize public safety.
3. Erosion and Sediment Control:
An urban drainage system aims to control erosion and sedimentation caused by stormwater runoff. By providing designated pathways for water flow, the system minimizes soil erosion and prevents sediment deposition in water bodies, protecting the quality of streams, rivers, and other receiving water bodies.
4. Water Quality Management:
Urban drainage systems incorporate measures to improve water quality by treating stormwater runoff. This includes the use of various treatment practices, such as filtration systems, bio-retention basins, and constructed wetlands, to remove pollutants and contaminants before the water is discharged into natural water bodies. The objective is to protect and enhance water quality, reduce the impact of urban runoff on ecosystems, and support sustainable water management practices.
5. Infrastructure Protection:
The urban drainage system aims to protect and preserve the integrity of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, buildings, and utilities. By effectively managing stormwater, the system helps prevent damage caused by flooding and excessive water infiltration into underground infrastructure, such as sewer systems and foundations.
6. Public Health and Safety:
The drainage system plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health and safety. By preventing stagnant water accumulation, the system reduces the breeding grounds for disease-carrying vectors such as mosquitoes. It also minimizes the risks associated with flooding, including property damage, contamination of water supplies, and the potential for accidents or injuries during extreme weather events.
7. Sustainable Urban Development:
An urban drainage system supports sustainable urban development by considering environmental and social factors. It promotes the efficient use of land, preserves natural hydrological processes, and incorporates green infrastructure elements to enhance water management practices. The system aims to balance urbanization with ecological considerations, resilience to climate change, and the overall well-being of communities.
In summary, the purpose and objectives of an urban drainage system revolve around effective stormwater management, flood prevention and control, erosion and sediment control, water quality management, infrastructure protection, public health and safety, and sustainable urban development. By fulfilling these objectives, the system ensures the resilience, functionality, and livability of urban areas.