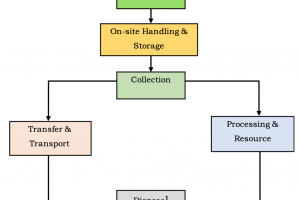
Factors Affecting Solid Waste Management System

Several factors influence the design and implementation of a solid waste management system. These factors vary from region to region and can significantly impact the effectiveness and sustainability of waste management practices.
Following are the factors affecting solid waste management system, its design, development, and operation:
- Institutional Factors
- Social Factors
- Financial Factors
- Economic Factors
- Technical Factors
- Environmental Factors
Institutional Factors
Institutional factors affecting solid waste management system involve laws and policies that allow the government to effectively implement Integrated Solid Waste Management. Steps that can be taken in this regard include:
- Establish a national and/or provincial policy and pass laws on SWM standards and practices.
- Identify the roles and responsibilities of each level of government.
- Ensure that the local governments have the authority and resources to implement an ISWM plan.
The presence and enforcement of legislative and regulatory frameworks play a vital role in shaping solid waste management practices. Laws and regulations govern waste collection, disposal, recycling, and the establishment of waste management infrastructure. Strong regulations and enforcement promote proper waste handling and encourage the adoption of sustainable waste management practices.
Social Factors
Social factors affecting the solid waste management system involve local customs and cultural/religious practices which can generally be affected or altered by sustained public education campaigns. The knowledge of these factors can determine how the waste is generated and disposed of. The local government must ensure citizen participation in all phases of management planning to help gain community awareness, input, and acceptance.
The level of public awareness and participation in waste management practices influences the success of waste management systems. Educating and engaging the public in waste reduction, recycling, and proper waste disposal practices can lead to improved waste management behaviors. Public involvement in waste management decision-making processes and community-based initiatives can enhance the overall effectiveness of waste management systems.
Population Density and Composition:
The population density and composition of an area affect the quantity and types of waste generated. Higher population densities generally result in increased waste generation, requiring efficient waste collection and disposal strategies. The composition of the population, including residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, affects the nature and characteristics of the waste stream.
Financial Factors
This is the most important factor to consider while implementing an ISWM plan. The source(s) of funds must be identified and/or created to help finance the SWM plan. In this regard, the local government should identify the sources that can provide funding for SWM, including general revenues or user fees, the private sector, government, and international agency grants and loans, etc.
The availability of financial resources and infrastructure affects the implementation and maintenance of waste management systems. Limited financial resources can impact the establishment of collection networks, waste treatment facilities, and recycling infrastructure. Adequate budget allocations and funding mechanisms are crucial to support the sustainable operation of waste management systems.
Economic Factors
Economic factors affecting the solid waste management system should be differentiated from the above, as these include the financial (more precisely, economical) output of the ISWM plans, for example, the jobs creation, enhancement of public trade and tourism, political mileage, etc. In order to evaluate these factors, the local government must calculate the initial capital investment requirements and long-term operating and maintenance costs associated with the various waste management activities. In addition, they must evaluate the public’s ability and willingness to pay for the services and evaluate activities based on effectiveness in handling waste potential for job creation.
Rapid urbanization and economic development contribute to increased waste generation due to increased consumption and industrial activities. Urban areas often require more sophisticated waste management systems to handle higher volumes of waste and address diverse waste types.
Technical Factors
These factors include the determination of equipment and facilities required for the implementation of the ISWM plan and more importantly, the locations where these equipment and facilities will be kept. The determination of these factors will depend on geological factors, transport distances, and projected waste generation, which will then become the basis for siting and design of various equipment and facilities.
Advances in waste management technologies and innovations play a significant role in improving waste management systems. Technologies such as waste-to-energy, composting, anaerobic digestion, and advanced sorting and recycling systems enhance waste treatment and resource recovery processes. Technological advancements can lead to more efficient and sustainable waste management practices.
Environmental Factors
Every ISWM plan has a deep impact on natural resources, human health, and the environment in general. All SWM activities such as landfilling or combustion must take into account the environmental cost of these activities and strive to minimize their effects on human health and the natural resources of the area. In this regard, the local government must establish procedures to verify the protection of groundwater and drinking water and monitor compliance with national standards to ensure that human health risks are minimized.
Environmental concerns drive the need for sustainable waste management practices. The desire to minimize environmental impacts, such as pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and soil and water contamination, influences waste management decisions. The emphasis on waste reduction, recycling, and resource recovery helps mitigate environmental impacts.
Credits: GIZ - DEUTSCHE GESELLSCHAFT FÜR INTERNATIONALE ZUSAMMENARBEIT