Types of Hospital Waste | Risk Waste, Non-Risk Waste

Types of Hospital Waste:
There are two types of hospital waste
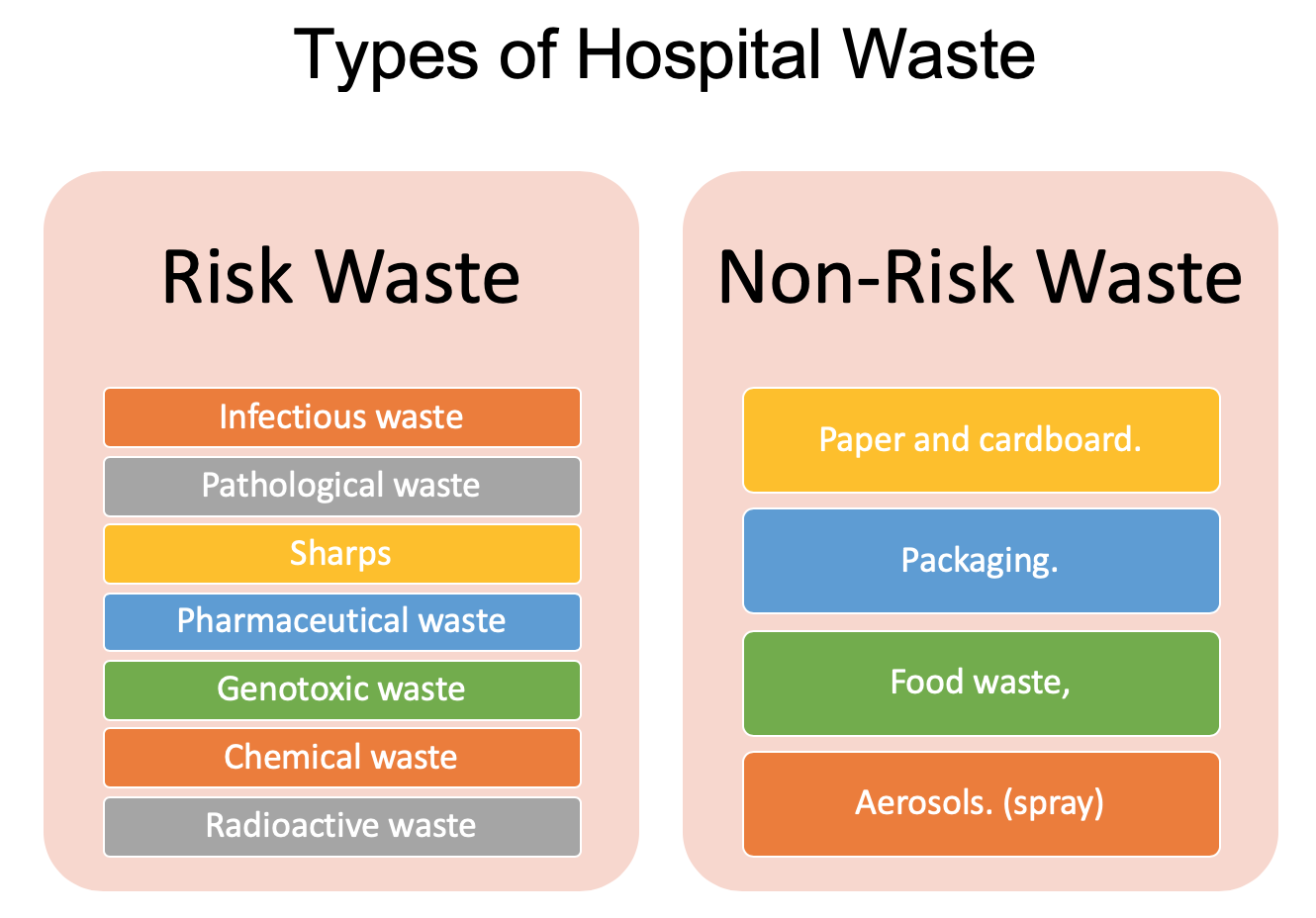
- Risk Waste
- Non-Risk Waste
Risk Waste:
Risk waste is further subdivided into seven (07) groups.
- Infectious waste
- Pathological waste
- Sharps
- Pharmaceutical waste
- Genotoxic waste
- Chemical waste
- Radioactive waste
Types of Hospital Risk Waste:
Infectious Waste:
This is the waste contaminated by any type of bacterium, virus, parasite, or fungi, which includes:
- Cultures (the growing of microorganisms in a nutrient medium (such as gelatin (Proteins from bone & skin) or agar) from laboratory work.
- Waste from surgery and autopsies (post-mortem).
- Waste from infected patients.
- Waste from infected hemodialysis patients.
- Infected animals from laboratories.
- Any material having been in contact with infected patients.
Pathological Waste
Pathological types of hospital waste include:
- Human or animal Tissues: Pathological waste may include human or animal tissues obtained during surgeries, biopsies, or autopsies. These tissues can carry infectious agents or contaminants and must be managed and disposed of appropriately. Proper handling and disposal of tissue waste involve packaging it in leak-proof, properly labeled containers or biohazard bags to prevent exposure and cross-contamination.
- Human or animal Organs: Pathological waste can encompass organs, such as excised human or animal organs from surgeries or post-mortem examinations. Similar to tissue waste, proper containment in leak-proof and labeled containers or biohazard bags are necessary. It is crucial to ensure that organic waste is disposed of safely to prevent the potential transmission of infectious diseases.
- Body parts: Body parts, including amputated limbs or other body components resulting from surgeries or trauma, are categorized as pathological waste. Safe management of body parts involves proper containment in suitable containers or biohazard bags to minimize the risk of exposure to infectious agents. It is crucial to handle and dispose of body parts with care and in accordance with local regulations and guidelines.
- Fetuses (Unborn Vertebrates): Pathological waste may include fetuses, which are unborn vertebrates, including human fetuses or animal embryos. Appropriate handling, containment, and disposal protocols must be followed to ensure the respectful and safe management of fetal remains. This may involve specialized containers, identification tags, and adherence to legal requirements and cultural sensitivities.
- Blood and body fluids: Pathological waste also encompasses blood and body fluids that may be collected during medical procedures, surgeries, or post-mortem examinations. These fluids can contain infectious agents such as viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens. Proper handling, containment, and disposal involve using leak-proof and labeled containers, such as biohazard bags or rigid containers, to prevent leakage and minimize the risk of contamination.
Sharps:
Sharps include the following whether infected or not:
- Needles: Needles are commonly used in healthcare settings for various procedures, such as injections, blood draws, and IV administrations. After use, needles should never be recapped or bent, as these actions increase the risk of needlestick injuries. Proper disposal of needles involves immediate placement into puncture-resistant sharps containers. These containers should be easily accessible, clearly labeled, and located close to the point of use to encourage safe disposal practices.
- Syringes: Syringes are used to deliver medications, and fluids, or extract bodily fluids. To ensure safe disposal, syringes should be separated from the needles and placed in designated sharps containers. If the syringe contains any residual medication, it may require additional steps, such as emptying the contents into appropriate containers and following local regulations and guidelines.
- Scalpels (A thin straight surgical knife used in dissection and surgery): Scalpels are surgical knives used for precise incisions during surgeries or dissections. After use, scalpel blades should be carefully removed from the handles using a safety mechanism or a blade remover. The blades should then be placed directly into sharps containers without recapping or bending.
- Infusion sets: Infusion sets consist of tubing, needles, and other accessories used for intravenous fluid administration. After use, infusion sets should be properly disposed of by placing the needles or sharp components into sharps containers. The remaining tubing and other non-sharp parts can be managed as regular medical waste following appropriate waste segregation protocols.
- Saws and Knives: Saws and knives may be used in surgical procedures or other medical interventions. These items should be handled with care during and after use. After use, saws and knives should be collected and stored in secure containers or bins to prevent injuries. They should be managed as sharp medical waste and disposed of following proper protocols.
- Surgical blades: Surgical blades are used for making precise incisions during surgeries. Similar to scalpels, after use, surgical blades should be carefully removed from the handles and placed directly into sharps containers without recapping or bending. The entire unit, including the blade and handle, may be disposed of as a single item if the blade is not detachable.
- Broken glass: Broken glass, such as vials, containers, or other glass medical equipment, can pose risks of cuts and injuries. It should be handled and disposed of with caution. Broken glass should be collected using appropriate tools (e.g., forceps or brooms) and placed in puncture-resistant and clearly labeled containers. It is important to avoid direct handling and ensure proper containment to prevent injuries during disposal.
- In addition to the above items, various other medical devices and instruments may pose risks of puncture, cuts, or injuries. Examples include lancets, trocars, catheters, and orthopedic pins. These items should be managed as sharps waste and disposed of in puncture-resistant sharps containers according to established protocols.
Pharmaceutical Waste:
 Pharmaceutical Wastes include:
Pharmaceutical Wastes include:
- Expired or unused pharmaceutical products.
- Spilled or contaminated pharmaceutical products.
- Surplus drugs, vaccines, or sera.
- Discarded items used in handling pharmaceuticals, for example, bottles, gloves, masks, and tubes.
Genotoxic Waste:
These wastes include:
- Cytotoxic drugs and outdated material.
- Vomiting, feces, or urine from patients treated with cytotoxic drugs or chemicals.
- Contaminated materials from the preparation and administration of the drugs such as syringes, vials (A bottle that contains a drug (especially a sealed sterile container for injection by needle), etc.
Chemical Waste:
These are disinfectants, solvents used for laboratory purposes, batteries, and heavy metals from medical equipment such as mercury from broken thermometers. Chemical waste can include the following:
- Chemicals from diagnostic and experiment work
- Cleaning processes
- Housekeeping and disinfecting procedures.
- Mercury waste such as from broken clinical equipment spillage.
- Cadmium waste, mainly from discarded batteries.
Radioactive Waste:
These wastes include Liquid, solid or gaseous waste contaminated with radionuclides generated from in-vitro (outside) analysis of body tissue/fluid, in-vivo (body organ imaging), and tumor localisations and investigations and therapeutic procedures. It can also consist of any glassware or other containers contaminated with radioactive liquids.
Non-Risk Waste:
Non-risk waste is that, which is comparable to normal domestic garbage and presents no greater risk, therefore, than waste from a normal home. This general waste is generated by almost everybody in the hospital, I.e., administration, patient risk, cafeterias rooms, cafeterias, and nursing station. Such waste may include:
- Paper and cardboard.
- Packaging.
- Food waste, i.e., leftover food, fruit, and vegetable peelings.
- Aerosols.(spray)