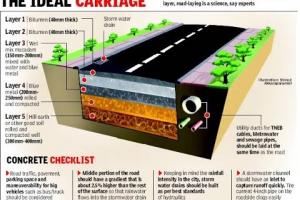
Typical Road Structure Details - Road Composition

Composition of Road Structure:
Road Structure Cross Section is composed of the following components:
- Surface/Wearing Course
- Base Course
- Sub Base
- Sub Grade
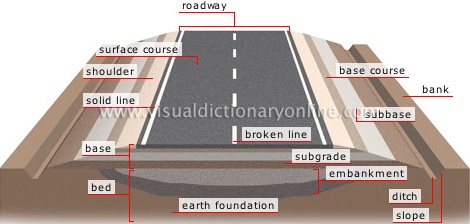
1. Surface/Wearing Course in pavement cross section:
The top layers of pavement which is in direct contact with the wheel of the vehicle. Usually constructed of material in which bitumen is used as binder materials.
a. Bituminous Pavement:
Consists of combination of mineral aggregate with bituminous binder ranging from inexpensive surface treatment ¼ in or less thick to asphaltic concrete. For good service throughout the full life bituminous pavement must retain following qualities.
- Freedom from cracking or raveling.
- Resistance to weather including the effect of surface water heat and cold.
- Resistance to internal moisture, particularly to water vapors.
- Tight impermeable surface or porous surface (if either is needed for contained stability of underlying base or subgrade).
- Smooth riding and non skidding surface.
The design should be done so that to meet the above requirements for considerable number of years (need proper design and construction supervision). Pavement meeting all the requirements above have been product if six distinctly different construction processes as follows:
- Heat a viscous bituminous binder to make it fluid, then in a plant mix it with heated aggregate place and compact the mixture while it is hot.
- Use fluid bituminous binder, mix it with aggregate at normal temperature. Mixing may be done at a plant (plant mix) or on the prepared roadway base (road mix). Spread and compact the mixture at normal temperature.
- Add solvent such as naphtha or kerosene to a viscous bituminous binder to make it fluid with aggregate at normal temperature by either plant or road mix methods. Spread and compact at normal temperature before solvent evaporates.
- Use fluid emulsion of viscose bituminous binder in water, mix it with aggregate at normal temperature by either plant or road mix method. Spread and compact at normal temperature before the emulsion breaks down with its components.
- Spread and compact clean crushed aggregate as for water bound macadam. Over it spray heated dissolved or emulsified bituminous binder which penetrates open areas of the rock and binds the aggregate together. Thus is commonly called “Penetration Method”.
- Spread bituminous binder over the roadway surface then cover it with properly selected aggregate. This is commonly called the “Inverted Penetration Method”.
Selections based on the requirements and economy, large volume of heavy vehicles, low traffic volume etc.
2. Base course
It is the layer immediately under the wearing surface (Applies whether the wearing surface is bituminous or cement concrete and or more inch thick or is but a thin bituminous layer). As base course lies close under the pavement surface it is subjected to severe loading. The material in a base course must be of extremely high quality and its construction must be done carefully.
Types of Base Course
- Granular Base Course
- Macadam Base
- In-water bound Macadam
- Treated Bases
3. Sub Base:
It is layer of granular material provided above subgrade generally natural gravel. It is usually not provided on subgrade of good quality. It is also called granular subbase.
a. Function of Sub base in Road Cross Section
- It enables traffic stresses to be reduced to acceptable levels in sub-grade in the Road Cross Section so that excessive deformation is prevented.
- It acts as a working plate form for the construction of upper pavement layers.
- Acts as a drainage layer, by protecting the sub grade from wetting up.
- It intercept upward movement of water by capillary action.
- It acts as a separating layer b/w subgrade and road base. By this it prevent the two layers from mixing up.
b. Characteristics of materials used in Sub Base:
The subgrade material should be clean and free from organic matter and should be able to be compacted by roller, to form stable sub-base. The material should have following characteristic.
- Well graded uniformity coefficient (D60/D10) should not be less than 3.
- Fraction passing sieve #200 shall not be greater than 2/3rd of the fraction passing sieve #40.
- Should have a L.L not greater than 25%.
- P.I not greater than 6
- CBR should not be less than 25.
 See also: CBR Test Procedure
See also: CBR Test Procedure - In coarse grain, aggregate retained by #10 sieve, %age of wear shall not be greater than 5%.
- The max dia of any particle shall not be greater than 2/3ed of the layer thickness of sub-base.
- Typical particle size distribution for the sub-base (granular) when will meet strength requirement are:
| B.S Sieve Size | % By mass of total Aggr. passing test sieve |
| 50 | 100 |
| 37.5 | 80 - 100 |
| 20 | 60 - 100 |
| 5 | 30 - 100 |
| 1.15 | 170 - 75 |
| 0.3 | 9 - 50 |
| 0075 | 5 - 25 |
* To avoid intrusion of silt and clay material in sub-base from subgrade
D15 (sub base) < 5 D15 (sub grade)
- Recommended plasticity characteristic for granular Sub Base (Road Note 31) are;
|
Climate |
Liquid Limit (L.L) |
Plasticity Index (P.I) |
|
Moist or wet tropical |
< 35 |
< 6 |
|
Seasonal wet tropical |
< 45 |
< 12 |
|
Arid & Semi Arid |
< 55 |
< 20 |
4. Sub Grade:
Consists of the naturally occurring material on which the road is built, or the imported fill material used to create an embankment on which the road pavement is constructed. Subgrades are also considered layers in the pavement design, with their thickness assumed to be infinite and their material characteristics assumed to be unchanged or unmodified. Prepared subgrade is typically the top 12 inches of subgrade.