Structural Bolts | Definition and Characteristics of Structural Bolts
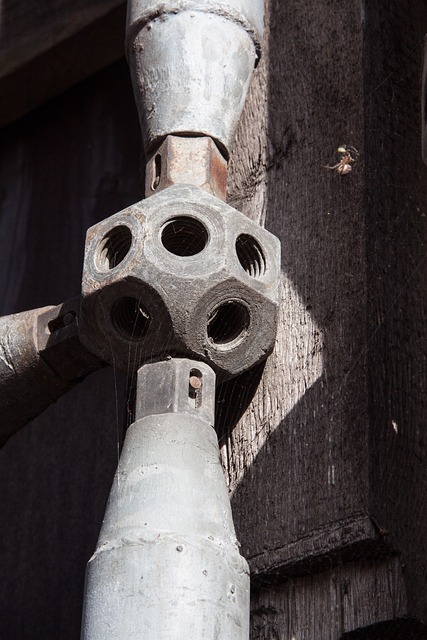

Definition
Structural bolts are a type of fastener specifically designed for use in structural steel connections. They are used to join structural members together, providing strength, stability, and load transfer in various construction projects. These bolts are engineered to withstand high loads and offer superior tensile and shear strength compared to standard bolts.
Characteristics of Structural Bolts
Here are some key characteristics and features of structural bolts:
1. High Strength:
Structural bolts are made from high-strength materials, such as medium carbon or alloy steel. These materials undergo specific heat treatments and mechanical processing to achieve the desired strength and durability required for structural applications.
2. Large Diameter and Length:
Structural bolts are typically larger in diameter and length compared to standard bolts. The larger size allows for increased load-bearing capacity and provides a secure connection between structural members.
3. Heavy Hex Head:
Structural bolts usually have a heavy hex head design. This larger head size distributes the load over a larger area and allows for better wrench grip during installation and tightening.
4. Unthreaded Shank:
Structural bolts have a portion of the shank that is unthreaded. This unthreaded section, known as the grip length, ensures that the bolt maintains a consistent clamping force and minimizes the risk of thread stripping or thread engagement issues during installation.
5. Pre-Installation Verification:
Before installation, structural bolts often undergo a pre-installation verification process. This involves checking the bolt dimensions, marking or stamping the bolt head with relevant identification codes, and ensuring the required mechanical properties and performance standards are met.
6. Installation Methods:
Structural bolts are typically installed using specific tightening methods, such as the turn of the nut method, calibrated wrench tightening, or direct-tension-indicator (DTI) tightening. These methods ensure that the bolts are properly tensioned to achieve the required preload and maintain the structural integrity of the connection.
7. Corrosion Protection:
Structural bolts are often coated or plated with corrosion-resistant materials, such as zinc, to enhance their longevity and protect against environmental factors.
Structural bolts are commonly used in various applications, including bridges, buildings, industrial structures, and other projects where reliable and strong connections are essential. Their design and performance characteristics make them well-suited for critical structural connections, providing the necessary strength and reliability to support the load-bearing requirements of the structure.