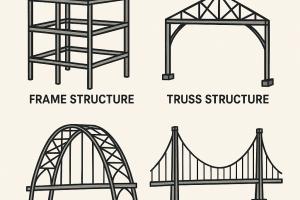
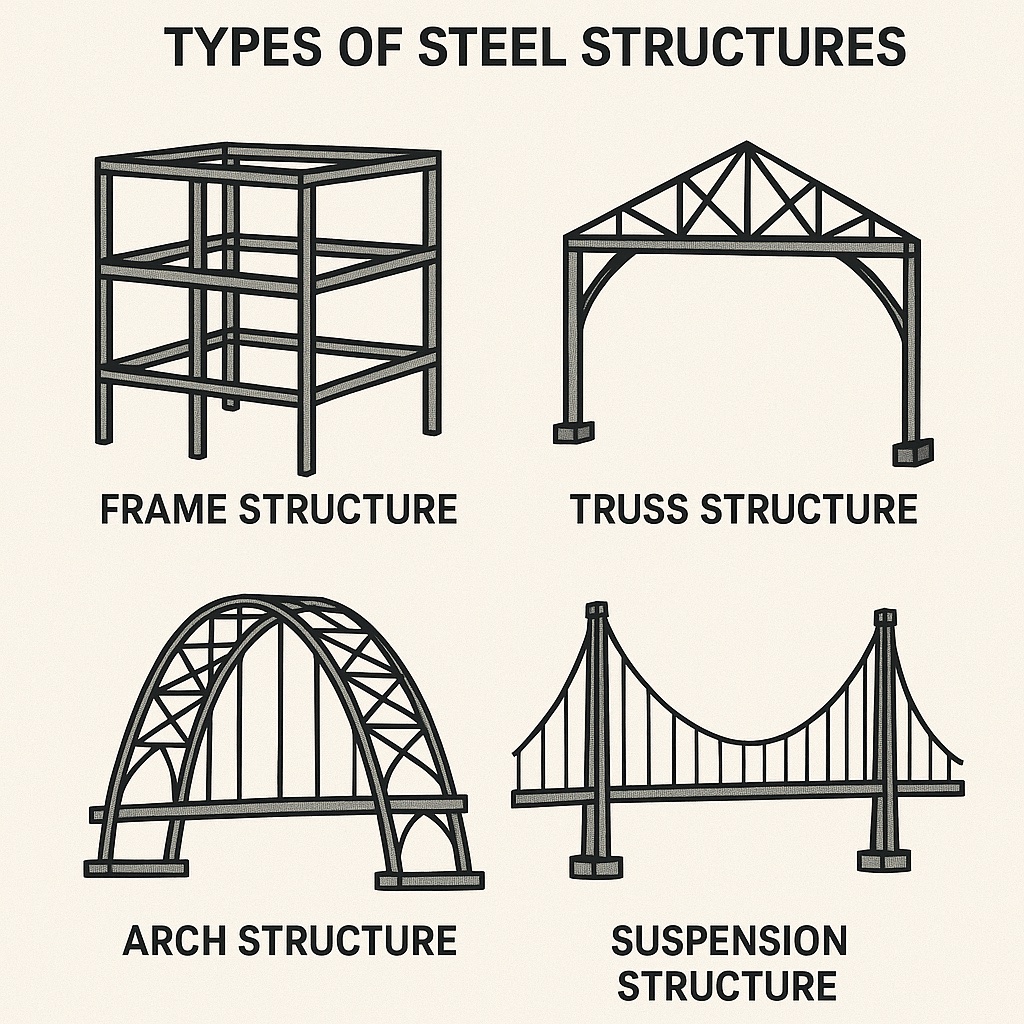
Types of Steel Structures
Classification of Steel Structures
Classification of Steel Structures involves categorizing them based on their structural behavior, design, and application. Here are brief explanations of different types of steel structures:
- Tension Members
- Compression Members
- Truss Systems and Frame Systems
- Built-up Members and Structures
- Shell Structures
- Suspension Structures
Tension Members:
Tension members are structural elements primarily designed to carry tensile forces. These members are subjected to axial forces that act in tension, resulting in elongation along the member's length. Examples of tension members include cables, hangers, and bracing elements that provide stability to structures under tensile loads. Primarily occur as:
- Chord Members in trusses
- In diagonal bracing in bracing systems
- Cable elements in suspension roofs, main cables of suspension bridges, and suspenders.
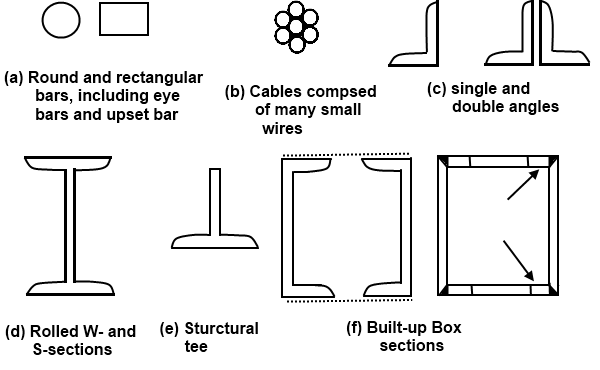
Compression Members
Compression members are structural elements designed to withstand compressive forces. These members are subjected to axial forces that act in compression, causing them to shorten or buckle. Common examples of compression members include columns, pillars, and vertical supports in buildings and bridges. Primarily Occur as:
- Columns in buildings;
- Chord Members in trusses and diagonal members in the end panels of trusses
- Stability is an important consideration in the design and behavior of compression members
- The area is generally spread out to maximize the Radius of Gyration
Truss Systems and Frame Systems:
Truss systems and frame systems are structural frameworks composed of interconnected members. Trusses consist of triangular-shaped elements, while frames have rectangular or square-shaped elements. These systems efficiently distribute loads and provide strength and stability to structures. Trusses are often used in roof structures, bridges, and towers, while frames are common in buildings and industrial structures.
Trusses are triangular units connected at joints, providing a high strength-to-weight ratio. Steel trusses are often used to span large distances without the need for internal columns. They distribute loads evenly and are resistant to deformation, making them ideal for roofs, bridges, and towers.
Applications: Roofs of large halls, railway bridges, and airport terminals.
Frame structures are the most common steel structures used in multi-story buildings and commercial complexes. These are made of vertical columns and horizontal beams connected rigidly to resist loads. Frame structures efficiently transfer loads to the foundation and are ideal for buildings requiring large interior spaces without intermediate walls or supports. Their modular nature allows for easy expansion and modifications.
Applications: Office buildings, shopping malls, high-rise apartments.
Built-up Members and Structures:
Built-up members and structures involve combining multiple steel sections or plates to form larger and stronger members. This technique allows for creating customized shapes and sizes to meet specific design requirements. Built-up members are used when standard rolled sections may not be sufficient, and they are commonly employed in large-span structures, industrial buildings, and heavy equipment supports.
Shell Structures:
Shell structures are characterized by curved or curved-like surfaces that form a continuous shell-like shape. These structures derive their strength from their form, with the load being evenly distributed across the surface. Steel shell structures can be seen in dome-shaped buildings, storage tanks, and curved roofs.
Shell structures are thin, curved plates that distribute loads in multiple directions, while space frames are three-dimensional truss-like systems composed of interconnected struts in a geometric pattern. Both systems offer lightweight and highly stable designs.
Applications: Airports, exhibition centers, stadiums.
Suspension Structures:
Suspension structures are characterized by a series of tension elements that support the weight of the structure, creating a suspended or hanging effect. Steel suspension structures often utilize cables or chains to suspend the main load-bearing members. Suspension bridges are a notable example of this type of structure.
Suspension structures use cables suspended between towers to hold the weight of the structure below. The main cables are anchored at both ends and carry the load through tension. This type of structure is highly efficient for spanning long distances and is often seen in bridge engineering.
Applications: Suspension bridges, transmission towers, and some types of roofs.
Steel structures offer versatile solutions for modern construction challenges. Their adaptability to various architectural styles, combined with their mechanical advantages, makes them a preferred choice for engineers and architects. Selecting the appropriate type of steel structure ensures not only safety and functionality but also cost-effectiveness and aesthetic appeal.