Types of GeoTextiles and GeoComposites

Geotextiles are permeable fabrics, generally made from fibers of Polypropylene, Polyester, Polyamide, and Polyethylene. Properties of Geotextiles of each type are different as well as the uses of geotextiles. The common types of Geotextiles are woven or non-woven.
Types of GeoTextiles
Woven Geotextiles
Woven geotextiles have interlacing filaments or yarns in two perpendicular directions - the longitudinal (or warp) direction and the crosswise (or weft) direction. Woven geotextiles often have greater tensile strength in the warp direction than the weft. Whereas non-woven fabrics are formed by linking filaments using:
- Heat bonding, in which filaments are melted together for bonding.
- Needle punching, in which needles are driven through the filaments to entangle them.
- Resin bonding, a setting resin is used to bond filaments together.
Geogrids
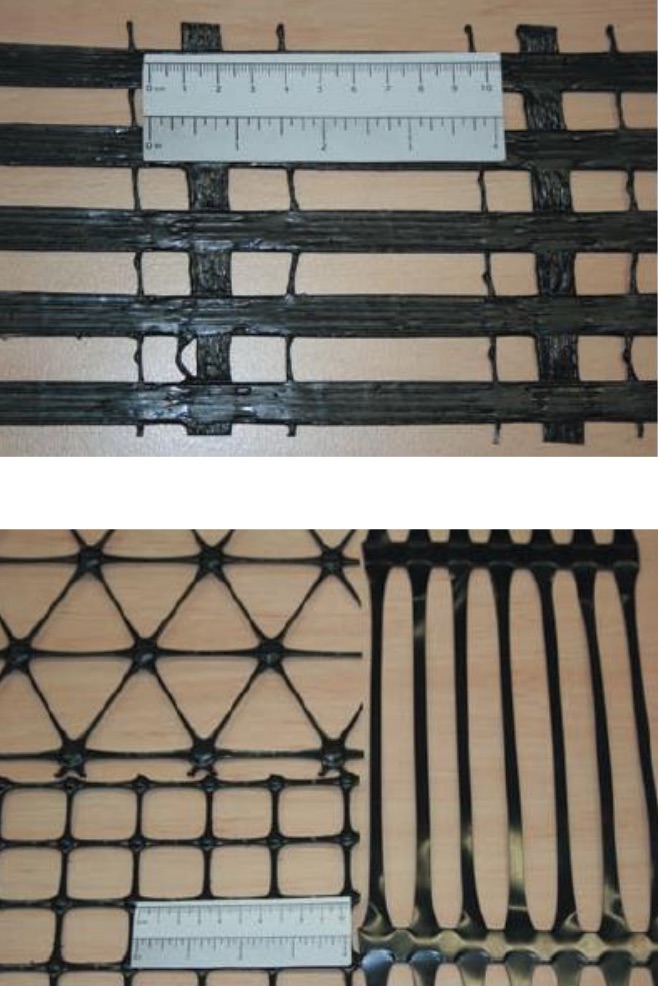
Geogrids are matrix-like materials made up mostly of longitudinal and transverse ribs. The aperture sizes are typically 10-200 mm in dimensions. The aperture size is designed large enough to allow larger particles to pass through the grid. This type of geosynthetic is mainly used for reinforcement.
The two main types of geogrids as per manufacturing process are:
- Welded mesh – Strands or tapes at right angles are welded at intersection points.
- Deformed (or extruded) grids–Sheets of PE or PP with punched holes are drawn to produce apertures.
Geomats
Geomats are three-dimensional, net-like open structured geosynthetics. They are usually made of monofilament polymers such as HDPE (High Density Poly Ethylene) and heat bonded at contact points. This type of geosynthetic is commonly used for re-vegetation and erosion control of the soil.
Geomembranes
Geomembranes have very low permeability and are used to control fluid or gas migration. They are made from relatively thin, continuous polymer sheets or impregnated geotextiles. Several methods exist to create textured geomembranes with improved surface friction.
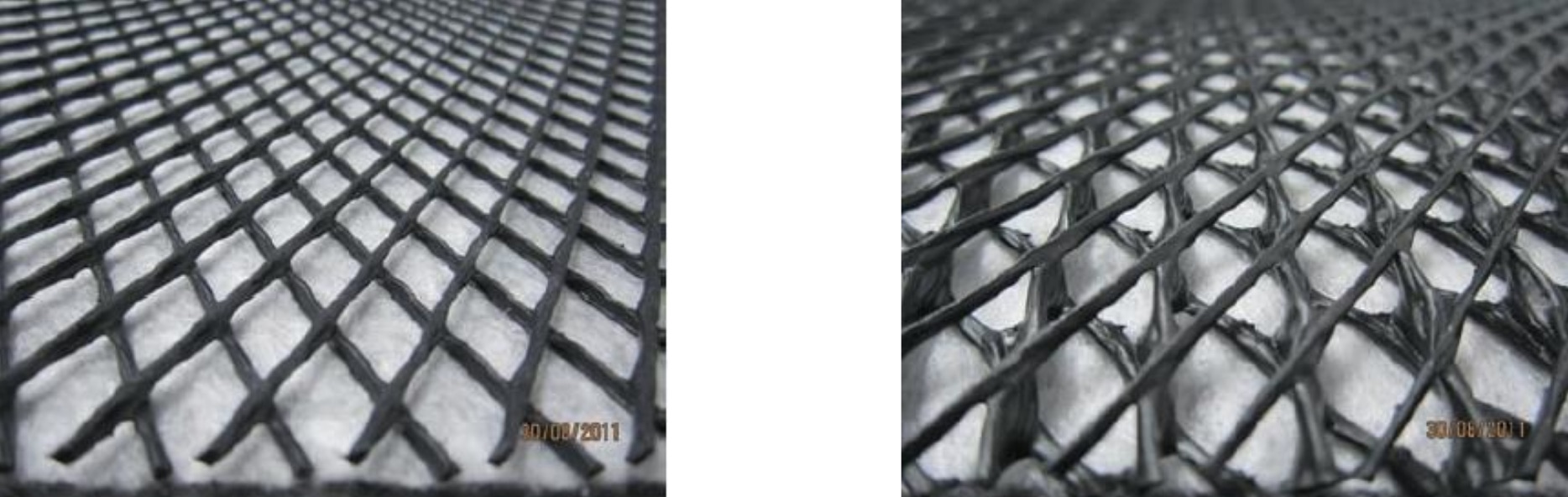
Geonets
Geonets are grid-like materials designed for in-plane drainage capability. They are used with a geotextile or geomembrane on either side to prevent soil intrusion and are typically made of PE resin.

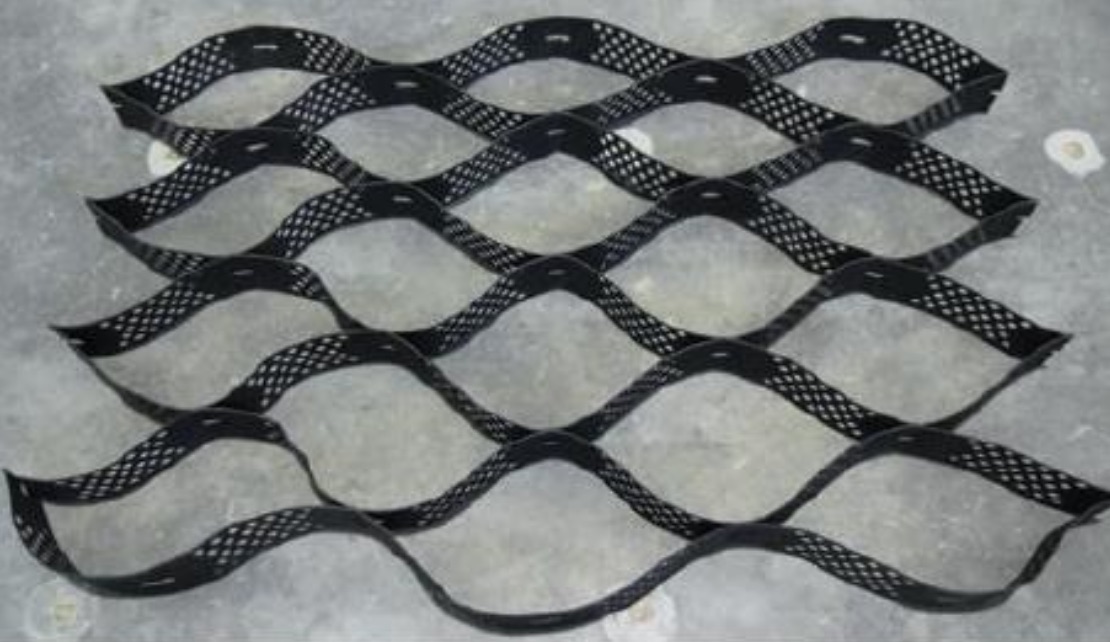
Geocells
Geocells are three-dimensional geosynthetics intended to provide physical soil confinement. The geocells are typically made of 100 mm wide and 1.2 mm thick HDPE strips welded at 300 mm intervals to form a cell like connected structure. These types are used for confinement and containment of materials.

Geocomposites
Geocomposites are made up of two or more materials stuck together. The common types are:
- Geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs) – Commonly used as liquid barriers.
- Prefabricated vertical drains (PVDs).
Geonet-geotextile composites are also of two types:
- Geopipes.
- Geofoams.