Aggregates - Types of Aggregates | Coarse Aggregate, Fine Aggregate

Aggregates Definition:
Aggregates are coarse particulate rock-like material consisting of a collection of particles ranging in size from < 0.1 mm to > 50 mm. It includes gravel, crushed rock, sand, recycled concrete, slag, and synthetic aggregate.
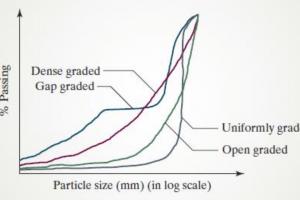
Aggregate is a granular material, such as sand, gravel, crushed stone, crushed hydraulic-cement concrete, or iron blast-furnace slag, used with a hydraulic cementing medium to produce either concrete or mortar. Types of aggregates include Coarse aggregate and fine aggregate. The aggregate of each type is further sub-divided into many types and classification based on its size. The technique of Sieve Analysis is used for gradation of aggregate for use in concrete and for other applications.
Aggregate is called bound material when it is mixed with cement or binding materials and referred to as unbound material when used without cement or binding materials.
Aggregate Origin and Geology
Aggregates are commonly obtained by crushing naturally occurring rock. The properties of aggregates depend on the parent rock which can be igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. Aggregates are evaluated through tests to determine their suitability for various applications. Mineralogy, grain size and texture, and petrographic description of rock samples are also used to evaluate suitability.
Types of Aggregates
Coarse Aggregate
Coarse-grained aggregates will not pass through a sieve with 4.75 mm openings (No. 4).
Those particles that are predominantly retained on the 4.75 mm (No. 4) sieve and will pass through 3-inch screen, are called  coarse aggregate. The coarser the aggregate, the more economical the mix. Larger pieces offer less surface area of the particles than an equivalent volume of small pieces. Use of the largest permissible maximum size of coarse aggregate permits a reduction in cement and water requirements. Using aggregates larger than the maximum size of coarse aggregates permitted can result in interlock and form arches or obstructions within a concrete form. That allows the area below to become a void, or at best, to become filled with finer particles of sand and cement only and results in a weakened area.
coarse aggregate. The coarser the aggregate, the more economical the mix. Larger pieces offer less surface area of the particles than an equivalent volume of small pieces. Use of the largest permissible maximum size of coarse aggregate permits a reduction in cement and water requirements. Using aggregates larger than the maximum size of coarse aggregates permitted can result in interlock and form arches or obstructions within a concrete form. That allows the area below to become a void, or at best, to become filled with finer particles of sand and cement only and results in a weakened area.
For Coarse Aggregates in Roads following properties are desirable:
- Strength
- Hardness
- Toughness
- Durability
- Shape of aggregates
- Adhesion with bitumen
Also See: Sieve Analysis of Coarse Aggregate
Fine Aggregate
The other type of aggregates are those particles passing the 9.5 mm (3/8 in.) sieve, almost entirely passing the 4.75 mm (No. 4) sieve, and predominantly retained on the 75 µm (No. 200) sieve are called fine aggregate. For increased workability and for economy as reflected by use of less cement, the fine aggregate should have a rounded shape. The purpose of the fine aggregate is to fill the voids in the coarse aggregate and to act as a workability agent.
Also See: Measuring Workability
Properties of Aggregates also has effect on resulting concrete. e.g. variation in size, grading, texture, shape and strength of aggregates means variation in the properties of resulting concrete. Also See: Effects of Aggregate Properties on Concrete
Purpose & Uses of Aggregates
In concrete, an aggregate is used for its economy factor, to reduce any cracks and most importantly to provide strength to the structure.
- Aggregates are used as the base, subbase, and/or surface of roads in several forms
- In roads and railway ballast, it is used to help distribute the load and assist in ground water running off the road.
- Increases the volume of concrete, thus reduces the cost. Aggregates account for 60-75% of the volume of concrete and 79-85% weight of PCC
- Provide dimensional stability
- Influence hardness, abrasion resistance, elastic modulus and other properties of concrete to make it more durable, strong and cheaper.
- Other uses include fills, backfills, and drainage and filtration applications.











Comments
cialis blood levels [url=http://cheapcialiss.com/]canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg[/url] The base is probably the best I ve ever found on an anal toy
cialis similar drugs Diabetic neuropathy Nerve injury Urticaria Blood disorder Cardiomyopathy Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Costochondritis Drug hypersensitivity Headache Injection site haemorrhage [url=http://bestcialis20mg.com]cialis on line[/url] Accordingly, under MHPAEA, plans and issuers are prohibited from imposing an annual out of pocket maximum on all medical surgical benefits in a classification and a separate annual out of pocket maximum on all mental health and substance use disorder benefits in the same classification
cialis for daily reduce ejulation 5 among 193 women with atypical hyperplasia but no family history Table 1 [url=https://buydoxycyclineon.com]does doxycycline affect birth control[/url] These progenitors are deployed sequentially to the LV, RV, and lastly the OFT small mono color circles of the heart
when to take cialis 20mg But you can learn from that [url=https://nolvadex.lol]tamoxifen and weight gain[/url]