River Training Works - Methods, Benefits and Functions
Introduction to RTW:
Rivers are magnificent forces of nature, meandering through landscapes, carving deep valleys, and nurturing ecosystems. However, their dynamic nature can also pose challenges, particularly in areas where human activities intersect with these water bodies. To manage and control their flow effectively, river training works play a crucial role. In this article, we delve into the significance of river training works, their methods, and the benefits they bring to both humans and the environment.
Understanding River Training Works:
River training works refer to a set of engineering techniques employed to regulate and modify the course of a river, enhancing its navigability, flood control, and water management capabilities. These interventions are carried out with careful consideration for the natural dynamics and characteristics of the river, aiming to strike a balance between human needs and environmental preservation.
Methods of River Training Works:
Dams and Barrages:
Dams and barrages are constructed across rivers to store water and regulate its release. By managing the water flow, these structures help prevent flooding during heavy rainfall or snowmelt and ensure a constant water supply for various purposes, such as irrigation, industrial use, and domestic consumption.
Embankments:
Embankments, also known as levees or flood banks, are raised banks built along the river's course to contain its flow within defined boundaries. They protect nearby settlements, agricultural lands, and infrastructure from floods, preventing damage and loss of life. Additionally, embankments can redirect the river's course, avoiding erosion and maintaining stability.
River Channelization:
Channelization involves modifying the river's path to improve its navigability, facilitate irrigation, and control erosion. By dredging or widening the river channel, obstacles such as sandbars and rocks can be removed, allowing for safer and more efficient navigation. Channelization projects often involve the construction of training walls or revetments to prevent bank erosion and maintain a stable flow.
River Training Structures:
Various structures are utilized as a part of river training works. Spur dikes, groynes, and wing walls are constructed perpendicular to the river's flow to redirect the water, control sediment deposition, and mitigate erosion. These structures help maintain a balanced and stable river system while preventing excessive scouring and bank erosion.
Benefits of River Training Works:
Flood Mitigation:
One of the primary benefits of river training works is flood control. By managing the flow and containment of water, these interventions reduce the risk of flooding in downstream areas. This protects lives, property, and valuable ecosystems located along the riverbanks.
Enhanced Navigation:
River training works improve the navigability of waterways, allowing for safe transportation of goods and people. By removing obstacles and maintaining a consistent flow, these interventions facilitate trade and economic growth in the regions connected by the river systems.
Water Resource Management:
Efficient water management is crucial for sustainable development. River training works enable the regulated release of water, ensuring a stable supply for irrigation, drinking water, and industrial use. By preventing excessive water loss or wastage, these interventions contribute to the conservation of this precious resource.
Ecological Preservation:
River training works can be designed to minimize their impact on the environment and preserve the natural ecosystem. By carefully considering the ecological needs of the river and its surroundings, these interventions can create habitats for various flora and fauna, maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
Conclusion:
River training works are essential engineering interventions that strike a delicate balance between human needs and environmental conservation. By controlling the flow, preventing flooding, enhancing navigation, and managing water resources, these interventions ensure the sustainable use and preservation of rivers. It is crucial to approach river training works with a comprehensive understanding of the river's natural dynamics, considering both short-term goals and long-term
Functions of River Training Works
It includes guide banks, marginal bunds, spurs, etc. Functions of river training works are:
- To provide and non-tortuous approach to the weir.
- To prevent the river from out-flanking the weir.
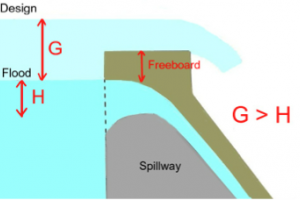
- To prevent additional areas to be submerged due to afflux.
- To prevent erosion of the river banks (protective works).
- To ensure the smooth and axial flow of water, to prevent the river from out ------ the works due to change in its course.
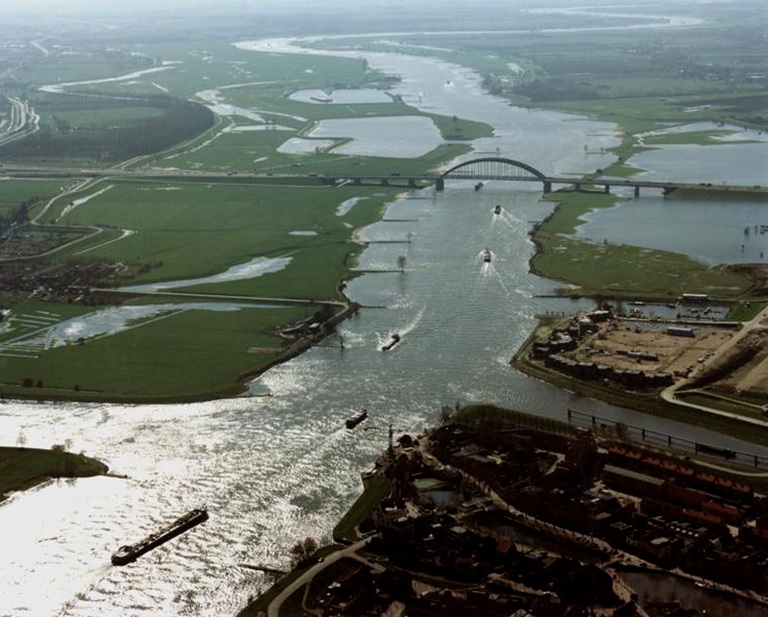
River Training Works
Guide banks:
Guide Bank are earthen embankments with stone pitching in the slopes facing water, to guide the river through the barrage, These river training works are provided for rivers flowing in planes, upstream and downstream of the hydraulic structures or bridges built on the river. Guide banks guide the river water flow through the barrage.
Guide banks force the river into restricted channel, to ensure almost axial flow near the weir site. (embankments in continuation of G-Banks. To contain flood within flood plains)
Marginal Bunds:
Marginal bunds are flood embankments in continuation of guide banks designed to contain the floods within the flood plain of the river. Both height and length vary according to back water effect caused by the barrage. They are not provided with stone pitching and fully cover the back- water length. Provided on the upstream in order to protect the area from submergence due to rise in HFL, caused by afflux.
Groynes or spurs:
Marginal bunds are also called as ‘Spurs’.
- Embankment type structures constructed transverse to river flood, extending from the banks into the river (also transverse dykes)
- Protect the bank from which they are extended by deflecting the current away from the bank.