Advantages & Disadvantages of Lateral Intake
When a certain amount of water is to be diverted from a river stream to some other location different types of structures are used such as weir, notches etc. Now to carry this amount of water to place where it can be used for some useful output different types of intake structures are used and the selection of a special Types of intake structures are chiefly distinguished by the method used to divert water from the river:
- Lateral intake
- Frontal intake
- Bottom intake
- Overhead intake (intake of the water via inlets arranged in piers)
Among these intake structures the overhead intake which is suitable for low-head power plants for energy production on large rivers. However, here we will be discussing smaller intake structures for small irrigation projects, small hydro-power plants, etc. Different types of intakes are used in different situations depending upon the:
- Amount of water to be diverted
- Amount of silt carried by the river
- Geomorphology of the river etc
Among these intakes lets discuss a common type of intake that is also commonly used in Pakistan.
Lateral Intake
Lateral intake can work in two scenarios
- Lateral intake with damming up o f the river
- Lateral intake without damming up of the river
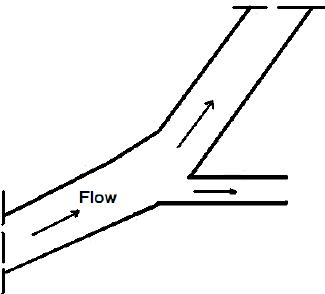
Simple picture of Lateral intake is given below
Simple picture of Lateral intake
Lateral Intake With Damming
A lateral intake with water damming normally consists of two structures, the weir and the intake. The weir is situated in the river and its function is to dam up the water level in order to ensure a constant minimum depth of water upstream of the weir and to allow the quantity of water for operational purposes (amount of service water) to be diverted from the river irrespective of the regime. Weir may be of different material/types such
- Concrete weir
- Crib weir
- Wooden weir etc
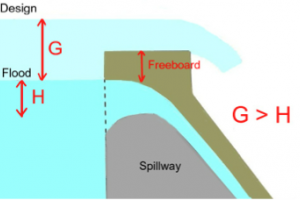
The intake structure in the form of a side weir prevents bed load from entering the power canal. If an excess amount of water enters the canal via the intake structure during a flood event, this is fed back into the river via a spillway (side weir, possibly with sluice in the canal to achieve a higher excess head) before it can enter the power canal.
Lateral Intake Without Damming
In most cases lateral intake without damming is suitable only for the diversion of small amounts of water. The inflow into the intake structure which is arranged laterally is directly dependent upon the water level in the river. According to the minimum regime of the river, the inflow is thus limited in quantity. Another limiting factor is that in the channel line the river bottom is normally situated at a lower level than the inlet bottom on the bank, with the result that in the inlet area, the excess head is smaller than the actual water depth of the river.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Lateral Intake
- Lateral intakes are favorable if the amount of water to be diverted is greater than 50% of the amount of water supplied.
- Lateral intakes are less favorable for very great to great gradient (I > 10%) as it may cause the scouring of downstream feeder channel. However it will result in maintenance free operation.
- For medium Gradient (1% > I > 0.01%) lateral intake is more favorable in connection with a hydraulically efficient sand trap as compared to bottom intake.
- If the ground plan of the river is straight then Lateral intake is less favorable in connection with additional structures.
- If the ground plan of the river is winding then lateral intake is very favorable when arranged on the outside bend.
- If the ground plan of the river is branched then lateral intake is Unfavorable as it will affect the damming action of the weir.
- For high concentration of the suspended matters in water lateral intake is suitable in connection with a hydraulically efficient sand trap.
- For low concentration of suspended matters in water lateral intake is well suited as compared to other intake structures
- For strong bed load transport lateral intake is less suitable as long as a sufficient amount of water remains in the river for flushing and transport purposes.
- For weak bed load transport lateral intake is well suited.